Blog | July 21, 2022
The Future of Derivatives Contracting Through Digital Transformation
The International Swaps and Derivatives Association, Inc. (ISDA).
ISDA was established in 1985 by a small group of dealers tasked with developing standard terms for interest rate swaps. It now has a membership of 980 member institutions from 78 countries. It has played a fundamental role in representing derivative market participants globally on derivatives issues, promoting a high standard of commercial conduct that fosters safe, efficient, and standardized markets for all users of over the counter (OTC) derivative products.
The early years.
In 1985, ISDA’s primary objective was to develop a standardized global documentation framework for trading privately negotiated bilateral OTC derivative transactions, predominantly interest rate derivatives.
The early ISDA legal framework included a master agreement containing credit terms relevant to the parties’ trading relationship, standardized confirmation templates for interest rate transactions, and definitions of key terms to document individual trades in different swap products.
The OTC derivatives industry has grown exponentially since those early years in terms of volume, complexity, and range of products, with the notional value of outstanding derivatives contracts at the end-December 2021 at $600 trillion [1].
In the past year, we have seen unprecedented turmoil in the financial system following years of increased focus on new regulations for cross-border OTC derivatives activities. Through this market activity, we may see greater adoption of derivatives for engaging with risk and position management, devising creative and sophisticated responses to these new challenges.
An innovative digital strategy underpins the future of derivative contracting.
The market infrastructure for derivatives faces a broad range of challenges. Regulation has driven significant improvements in post-trade processes. Still, legacy technology, a proliferation of disparate unstandardized legal and transaction data and an over-dependence on costly, manual intervention across front-to-back operations hinder progress. These issues, combined with ongoing regulatory uncertainty and increased pressure from compressed margins, require additional focus on a standard industry blueprint for a simplified target state for the entire post-trade process.
With so much work still to undertake in the post-trade space, it’s easy to understand why organizations might overlook efforts to digitize ISDA derivatives documentation. But worryingly, many legal disputes (over 80% in relation to collateral disputes) are due to inconsistency of legal data representation across contracts and systems, mainly because derivatives documentation continues to be overwhelmingly reliant on paper and PDFs, necessitating legal data to be manually re-keyed in downstream systems or sourced from outside of the contract itself. There is a proliferation of legal data available across contracts. Still, few organizations have harnessed technologies such as AI-based contract analytics to maximize their potential and use it to improve straight-through-processing in downstream systems.
So much of the current derivatives contracting process is still manual, including the legal documents and definitions that underpin this market, which relies heavily on bespoke, paper-based documentation, physical document exchange and wet-ink signatures, which add to the complexity and risk of the process. As organizations come under additional pressure to increase efficiencies and reduce risk and costs, greater standardization and automation will be fundamental.
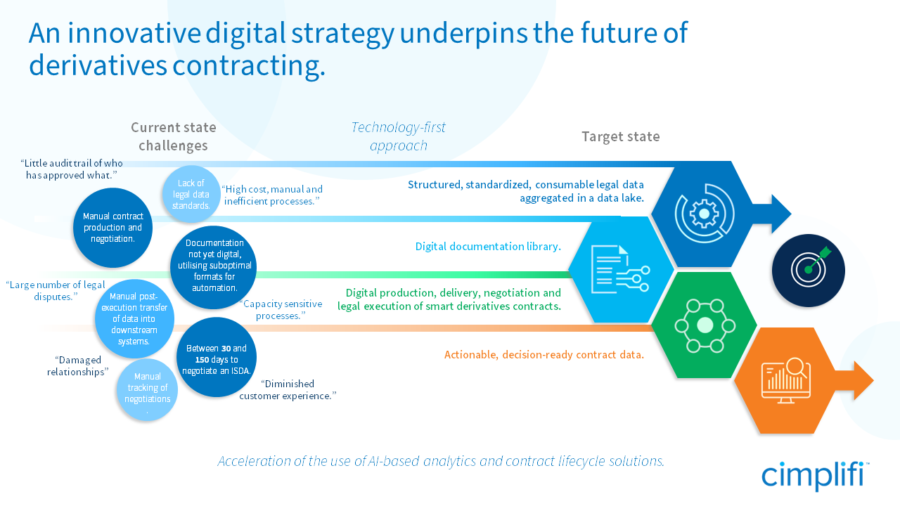
Several initiatives are underway to digitize derivatives documentation, enabling the industry to move towards a fully automated operating environment. We see five target state objectives for market participants:
1. Structured, standardized, consumable legal data aggregated in a data lake.
Comprised of industry-led data standards in digital formats that are structured, transparent, consumable and provide uniformity in machine-readable text. Housed in a data lake that allows for the aggregation of large, structured data sets, which will further accelerate the use of AI-based analytics and solutions.
Preconditions:
Industry consensus on which terms, events, provisions, conditions, fallbacks etc., can be standardized, allowing for a digital representation of these elections to be created.
2. Digital documentation library.
A comprehensive, up-to-date digital library in multiple languages of essential ISDA documentation, definitions, matrices, and templates to facilitate greater automation. A searchable operationalized repository makes it easier to deploy AI analytics to search for key terms and undertake comparisons across current and prevailing document versions.
Preconditions:
To be constructed to avoid stylistic drafting tables to enable better data extraction and analysis using AI. In the past year, ISDA has published its 2021 ISDA Interest Rate Derivatives Definitions and 1998 FX and Currency Option Definitions as natively digital definitional booklets, creating significant efficiencies in how organizations use and interact with the definitions, reducing complexity and the potential for error. However, there is still some way to go in digitizing existing documentation.
3. Digital production, delivery, negotiation, and legal execution of derivatives contracts.
Standardized elections reconciled by intelligent automation, customizable bilaterally negotiated clauses and smart contracts automatically populated with legal, risk and trade data and an AI/intelligent automation algorithm to perform the procedural fulfilment. All within a system that captures, processes and stores data to provide a complete digital record that users can interrogate with AI contract analytics.
Preconditions:
Legal and trade data standards in digital contracts are an essential precondition—a full deterministic definition of every contract election to allow for automation of elections.
4. Actionable, decision-ready contract data.
A single source of truth for automatic post- execution consumption in downstream collateral management, netting, contingent funding, transaction documentation and risk systems. Automated management information and tracking will drive richer insights into patterns and trends.
Preconditions:
Standardized legal and trade data, interoperability across the global derivatives infrastructure and uniformity in machine-readable text.
5. Solution to monitor and determine the occurrence of an incident that might give rise to an event of default or termination event.
Ability to monitor certain types of external and internal activity or data through oracles.
ISDA and its members have pushed the market along the digital path with recent developments, including launching its first-ever digital definitions. As ISDA develops its digital strategy, there are a few important considerations:
- Ongoing partnership with technology and solution providers to leverage advanced technologies such as AI-based contract analytics, lifecycle management, intelligent automation, and machine learning solutions.
- A laser focus on industry standards facilitates the adoption and migration to sustainable digitization. Real digital transformation is only possible through common underlying standards.
The future of derivatives contracting is electronic documentation, electronic signatures, smart legal contracts, and on-chain records utilizing legal data that provides a single source of truth for actionable and automatable insights.
To learn more about the CALMTM practice at Cimplifi and our expertise in contract analytics and lifecycle management click here. #keepCALMandcontracton
[1] BIS OTC derivatives statistics at end-December 2021